Mixer Examples
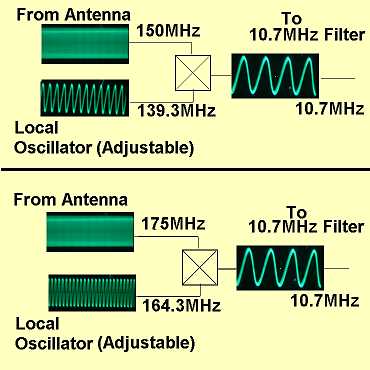
Here's a couple of examples to make things clearer. Arriving from the antenna (
via the rf amplifier)
is a multitude of frequencies ranging from, perhaps 50 MHz up through 700 MHz.
In the first example, we want to receive the signal at 150 MHz so we set our local oscillator frequency to 139.3 MHz. The resulting output from the mixer is 150.0 - 139.3 = 10.7 MHz.
In the second example, we want to receive the signal at 175 MHz so we set our local oscillator frequency to 164.3 MHz. The resulting output from the mixer is 175.0 - 164.3 = 10.7 MHz.
If we follow this with an amplifier which only amplifies signals at 10.7 MHz, then, provided our local oscillator is accurate, we must be amplifying the 'descendant' of the radio frequency we want.