Giving Your Computer A Fixed LAN IP Address
As I stated previously, when your computer's LAN IP Address is assigned automatically by the modem/router, there is a risk that it could be assigned the wrong address for the port forwarding to work and the way to avoid this happening is to give the computer a fixed LAN IP Address. In order to do this, you need two pieces of information:- The current automatically-assigned LAN IP Address of the computer.
- The same computer's MAC address.
As I wrote earlier, your computers connect to the modem/router through a piece of hardware called ethernet (or LAN). Sometimes this hardware is on a separate plug-in PCI card and sometimes it has been incorporated into the motherboard's hardware.
Built into the hardware is a "serial number" (The MAC, or Media Access Control Address) which other computers (and the modem/router) on the network are able to ascertain. Suffice it to say here that this MAC address is guaranteed totally unique to your individual bit of hardware. The same MAC address does not occur anywhere else on the planet! For our purposes, it could be regarded as a bit of "security over-kill" that we should need both the computer's LAN IP address and the computer's LAN card's MAC Address. But, remember, your LAN IP Address is far from unique - there are literally tens of thousands of computers using the same address - so your modem/router is right to ensure that incoming traffic is only routed to our LAN IP Address, which it does by confirming the corresponding MAC Address.
A DOS Window and ipconfig /all
Luckily Windows XP provides the tool we need to find the computer's LAN IP Address and its ethernet MAC Address. From the All Programs menu, select Accessories and click on Command Prompt. When the command window opens, type ipconfig /all and hit the 'Enter' key. A display similar to the one below should appear. It's similar to the previous one we saw except, this one shows a bit more information:
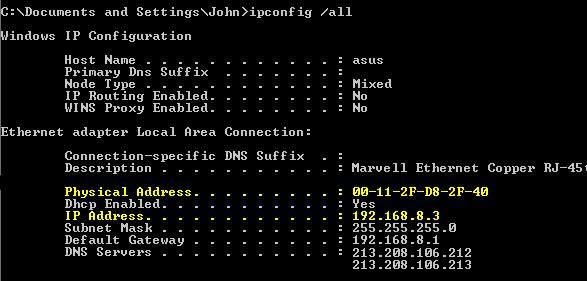
I've highlighted, in yellow, the two pieces of information we need. Note that Windows calls the MAC Address, the "Physical Address". Some modem/routers will actually be able to find the MAC Address for us but others can't so we may as well make a note of it from here. Incidentally, note the Default Gateway is actually the LAN IP address of the modem/router. There may be a couple of entries for the DNS Servers. if so, make a note of those. We may need them later.
As we did earlier, select Control Panel then double-click Network Connections. Highlight the entry shown as Local Area Connection, right-click on it and select Properties. Highlight the entry: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
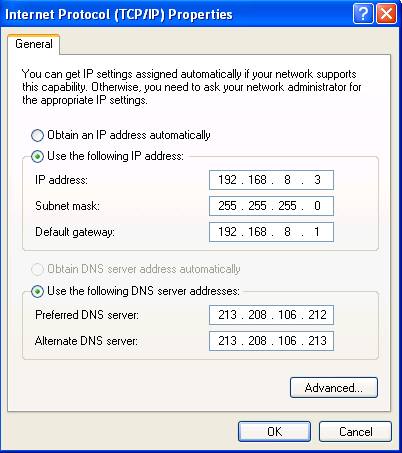 |
The next window should look like the window in this picture only, this time, we need to select the
Use the following IP address radio button. The text-entry boxes will become 'enabled' and we can now copy the information we obtained from the Command Prompt window. The Subnet mask will be filled in automatically for you. Also check the Use the following DNS server addresses radio button (if it hasn't already selected itself) and enter the DNS addresses also. If the Command Prompt window didn't list any DNS servers, the ones to use are the Primary and Secondary DNS servers which should be supplied by your ISP. If you don't know what they are, you can use the same address as the Default gateway entry for the Preferred DNS server and leave the Secondary DNS server blank. |
Open a Command Prompt window and type ipconfig /all again. The window should show all the settings you've just made and note that the Dhcp entry is now shown as 'No', whereas before it said 'Yes'. This means that the computer will no longer ask the modem/router for its LAN IP Address - instead it will use the one we've assigned here.
We now need to tell the modem/router about this computer and we need to ensure the modem/router doesn't issue this LAN IP Address to another computer...
© Copyright